What is Gynecomastia?
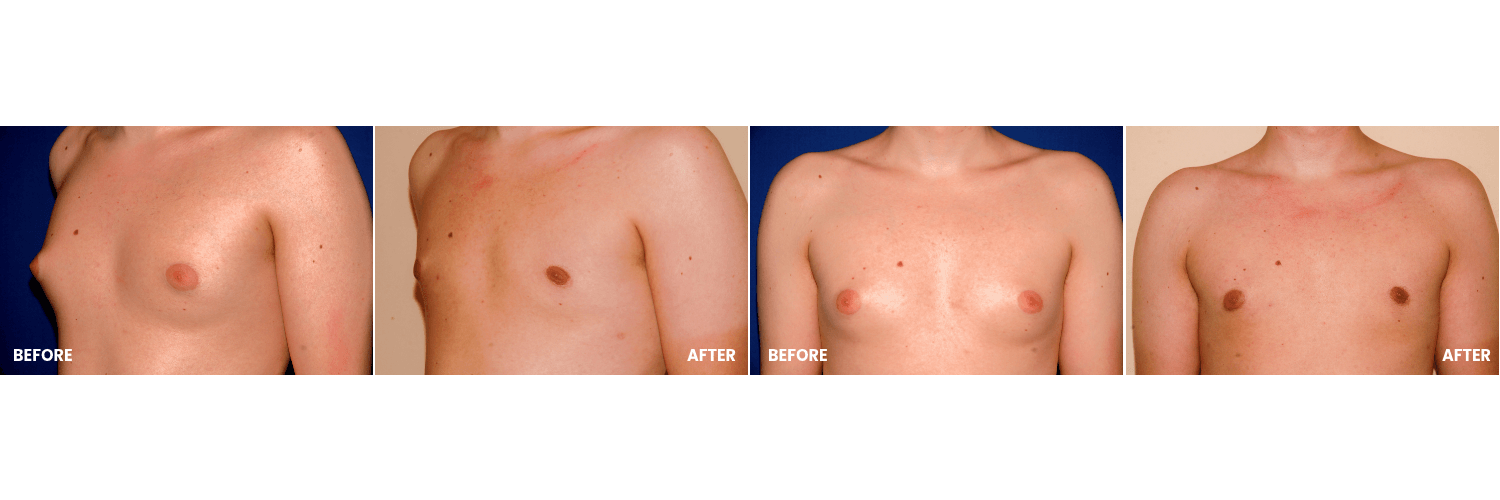
In “true” gynecomastia, glandular breast tissue grows in men, causing the chest to become visibly enlarged. This can often have a negative impact on the affected individual’s psychological well-being. Adolescents in particular often experience a strong sense of shame, which can sometimes go so far that they feel unable to enter into a relationship. Some men report a feeling of tightness in the chest, and in rare cases, mild pulling pain may occur.
Depending on the severity of the gynecomastia, the surgical correction can be performed on an outpatient, day-clinic, or inpatient basis.
Types and Treatment of “True” and “False” Gynecomastia
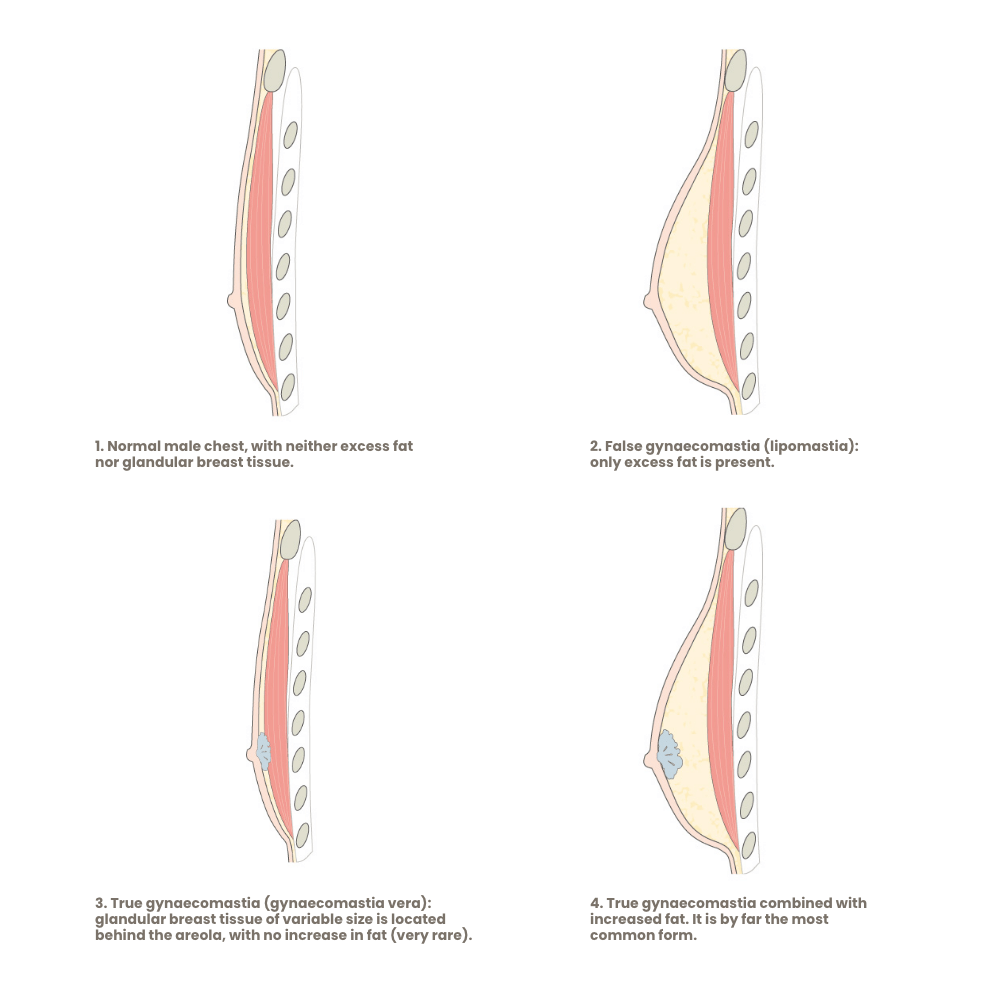
In true gynecomastia (gynecomastia vera), there is a benign enlargement of the glandular breast tissue in men. It may occasionally occur on only one side, but usually, both sides are affected—often to differing degrees. Gynecomastia is not a disease but rather a natural remnant of puberty in young men.
The so-called “false” gynecomastia, also known as pseudogynecomastia (the correct term is lipomastia), is caused solely by an accumulation of fatty tissue behind the nipple area and is never pathological.
Both pure gynecomastia and isolated lipomastia are relatively rare. In about 95% of all cases of enlarged male breasts, mixed forms are found—meaning glandular breast tissue behind the nipple in combination with excess fat tissue.
Gynecomastia – Facts and Key Information
Below you will find important details about the causes and different forms of gynecomastia.
What Does Gynecomastia Look Like?
Gynecomastia can be more or less visible on the bare upper body, depending on its degree of severity. When it is only mildly pronounced, it is usually noticeable from the side or in a half-profile view—about a 45° angle of the torso—where the protruding nipple becomes apparent while the turned-away side forms the body’s contour.
When the condition is more pronounced, the bulge is visible even under tight-fitting clothing (e.g., a T-shirt), and in extreme cases (comparable to a B or C cup in men!), it can hardly be concealed. As mentioned earlier, gynecomastia is almost always not a disease, though in rare cases it can result from a pathological hormonal imbalance.
Because men with glandular breast tissue can develop breast cancer, the cost of removing glandular tissue in cases of gynecomastia vera is covered by Austrian social insurance. Therefore, the presence of glandular breast tissue in men is officially recognized as a medical condition—even when the underlying cause is not pathological.
Causes of (True) Gynecomastia
Non-Pathological Gynecomastia
Every second man has small clusters of glandular breast cells located behind the areola. If these cells possess a positive hormone receptor for estrogen (a female sex hormone that is also produced in small amounts in the male adrenal glands), they will grow and enlarge when estrogen levels in the blood increase.
This is exactly what happens during puberty: in young men, testosterone levels rise as part of normal pubertal development. The body perceives this as a temporary hormonal imbalance and, in response, the adrenal glands produce more estrogen to compensate. As a result, the glandular breast cell clusters increase in size during puberty—provided the estrogen receptor is active.
After puberty, testosterone levels gradually decrease again, as does estrogen, leading to regression of the glandular tissue. However, this regression does not always occur: in approximately one out of every 100 men, this regression fails, leaving behind a “true” gynecomastia. This condition is neither dangerous nor pathological.
Neonatal Gynecomastia
A similar phenomenon occurs in newborns due to the effect of placental hormones on the breast tissue. This form of gynecomastia usually resolves on its own within a few weeks.
Age-Related Gynecomastia
With age, the natural decline in testosterone levels leads to a compensatory increase in luteinizing hormone (LH), which in turn stimulates the adrenal glands to produce more estrogen.
Frequency of Gynecomastia
Up to 1% of adult men (one in a hundred) are affected by gynecomastia, with around 95% of cases being mixed forms (glandular tissue and excess fat). Approximately 60% of adolescents experience temporarily enlarged breast tissue during puberty, particularly around the age of 14.
The Pathological Gynecomastia
The causes can vary but are fundamentally similar: any pathological alteration in the male hormonal balance can lead to true gynecomastia if it results in reduced testosterone production or an excess of the female hormone estrogen.
Because breast gland tissue is highly sensitive to hormonal fluctuations, any disturbance in the hormonal equilibrium can promote the growth of male breast tissue. Therefore, all conditions that affect hormonal balance are considered risk factors for true gynecomastia.
This hormonal imbalance can have various underlying causes:
- Pituitary gland tumors
- Adrenal gland tumors
- Androgen resistance (lack of testosterone effect despite normal hormone production)
- Klinefelter syndrome (a congenital chromosomal abnormality with underdeveloped testes, 47-XXY)
Since the liver plays a key role in breaking down hormones such as estrogen, chronic liver diseases like liver cirrhosis can lead to an excess of female hormones.
Chronic kidney dysfunction (renal insufficiency) can also affect hormone regulation by impairing the kidneys’ filtering function.
The loss of one or both testicles can similarly cause true gynecomastia, as the resulting imbalance between estrogen and testosterone levels stimulates glandular breast growth.
Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can also alter hormone balance and promote gynecomastia.
Overweight and Poor Nutrition
Gynecomastia often occurs in men who are overweight (obesity). In this case, the likely cause is the increased fat tissue, which stores estrogen. More fat means higher estrogen levels, which in turn promotes breast growth — naturally accompanied by more fat tissue.
Conversely, anorexia can also lead to gynecomastia due to a drop in testosterone levels.
Cosmetic Products, Medications, or Drugs
Certain medications, drugs, and even cosmetic products can trigger gynecomastia. Antidepressants, antibiotics, and heart medications can all disrupt hormone metabolism. Long-term use of heroin, marijuana, or alcohol can likewise cause hormonal changes that result in true gynecomastia.
A common cause of drug-induced gynecomastia is the use of anabolic steroids, frequently seen in bodybuilders.
Some hair and skin care products contain small amounts of synthetic female hormones, which can be absorbed through the scalp or skin into the bloodstream. Chemical compounds found in tea tree oil and lavender oil (if not 100% natural) are also suspected of acting like estrogens — all of which can contribute to true gynecomastia.
Hormonal Changes
In young adult men, normal estrogen levels range from 20 to 40 picograms per milliliter of blood, while normal testosterone levels are around 6 nanograms per milliliter.
The testosterone-to-estrogen ratio is therefore approximately 200 to 300.
If pseudogynecomastia develops due to age-related weight gain, fat often accumulates in the chest area. However, benign fatty tumors (lipomas) can also be the cause.
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia
If a man notices breast enlargement or feels a firm area behind the areola, he should seek medical evaluation. The most important diagnostic steps include:
- Mammography
- Ultrasound examination of the breast
- Hormone analysis (hormone profile)
If the hormone profile is abnormal, the underlying cause must be identified and treated before surgery is considered.
To distinguish between pseudogynecomastia and true gynecomastia, the physician will palpate the breast — this helps determine whether glandular tissue or only fat is present. The diagnosis can be further confirmed through ultrasound and mammography.
If gynecomastia has been present since birth or if no clear cause can be found, a chromosomal analysis may be useful to rule out genetic abnormalities. However, due to cost, this test is typically only performed when there are other indications of a possible genetic disorder.
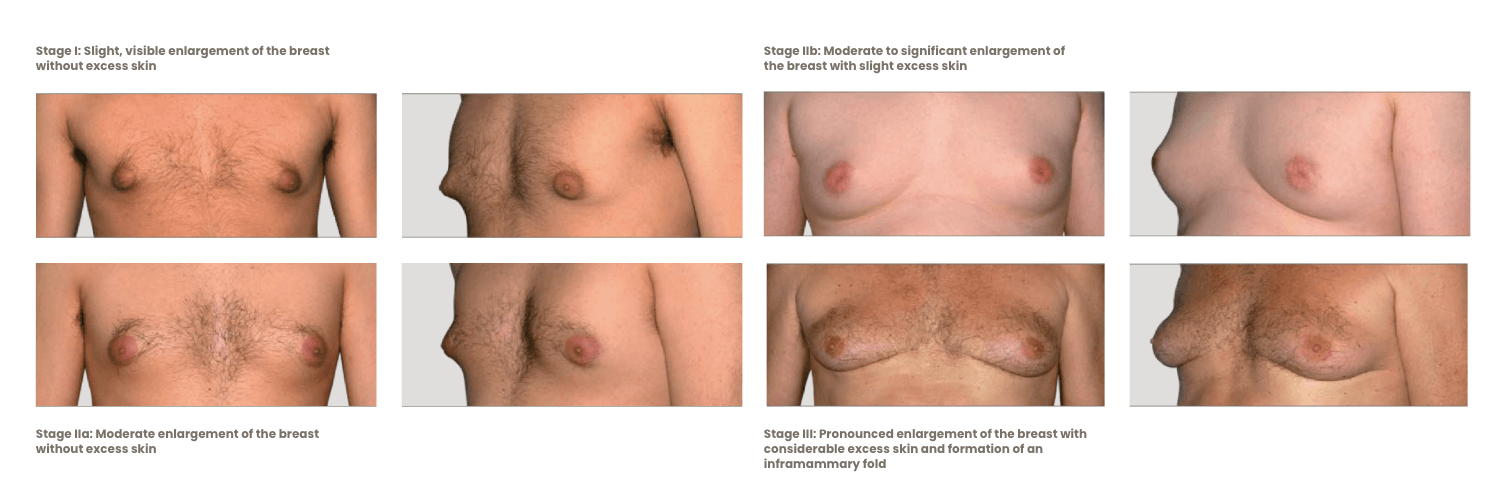
Stages of Gynecomastia
If the diameter of the male areola exceeds 3 cm, gynecomastia is often present as well.
The growth of the breast can be classified into five Tanner stages based on the size and shape of the nipple and areola:
- B1: The glandular breast tissue is palpable.
- B2: The glandular tissue becomes raised, and the areola enlarges.
- B3: The glandular breast tissue is larger than the areola.
- B4: The areola becomes elevated, and the glandular tissue appears firm.
- B5: At this stage, the male breast resembles a fully developed female breast.
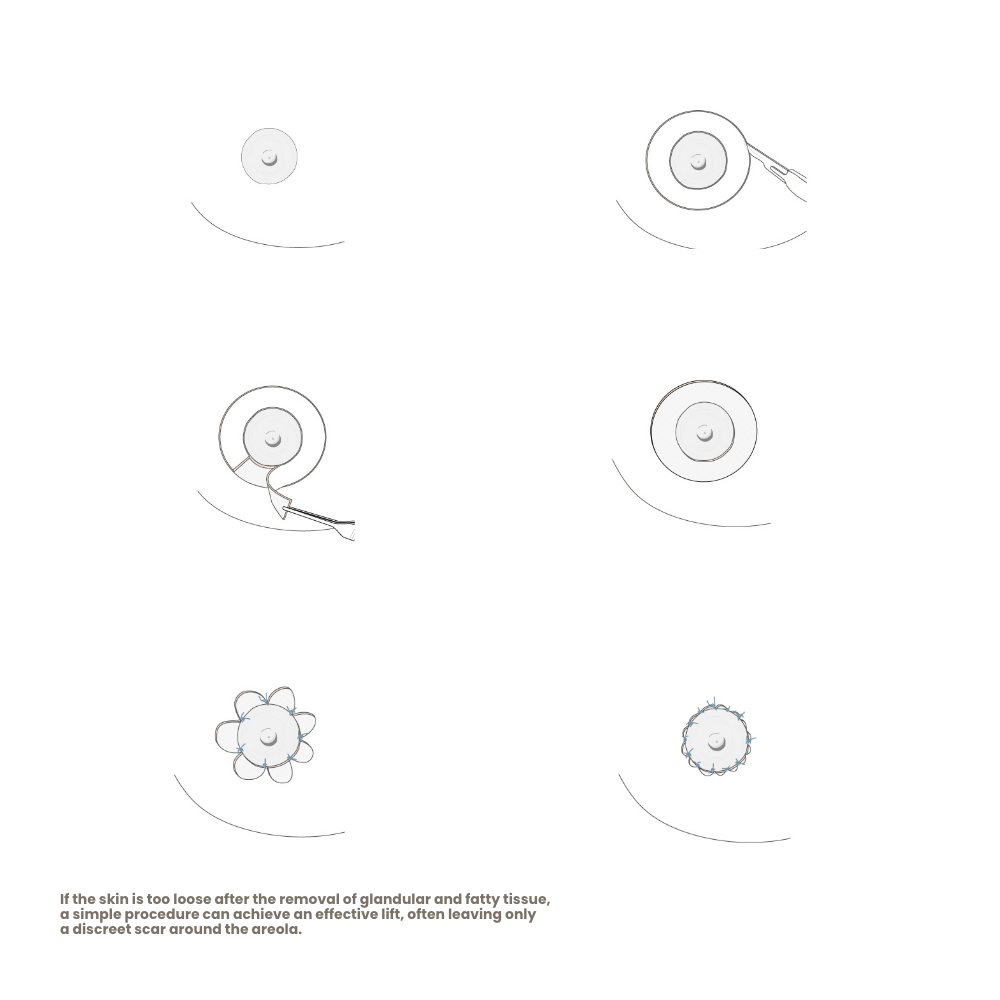
Correction Options for the Male Chest
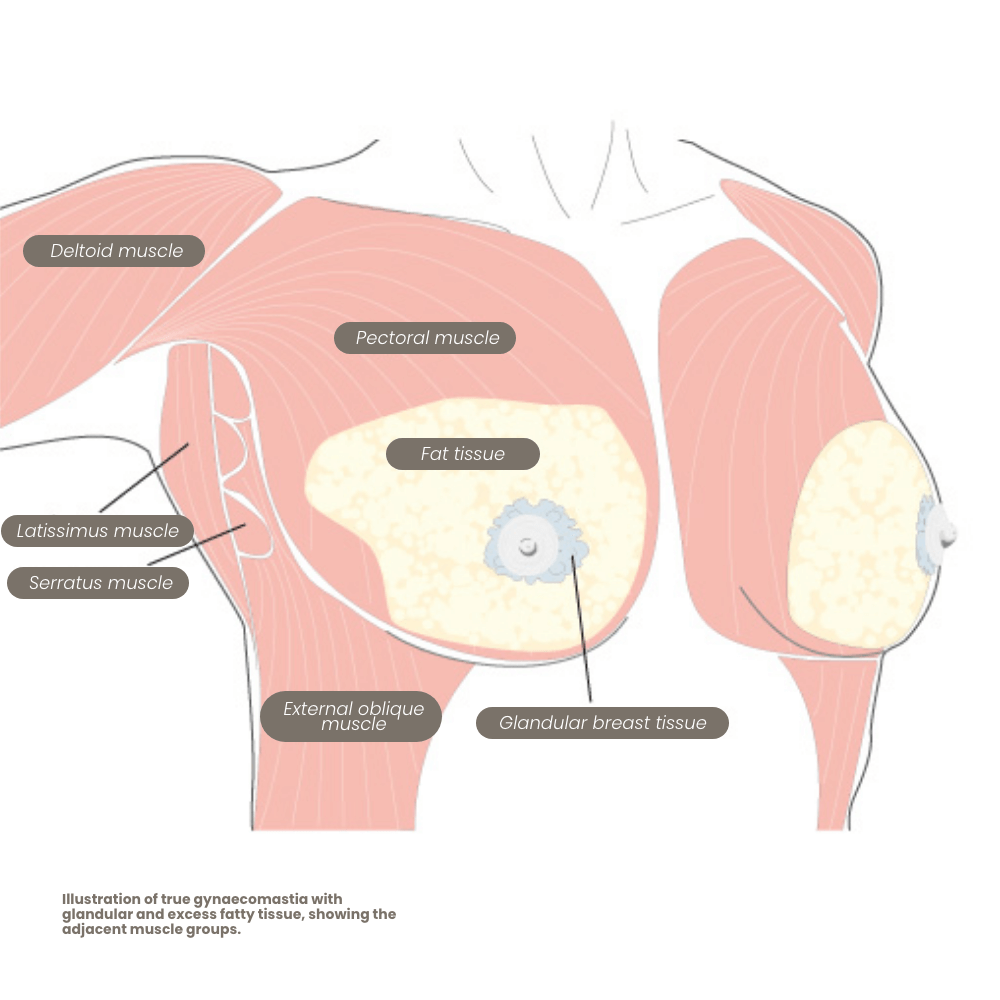
If glandular breast tissue is detected, surgical removal can be performed with cost coverage by social insurance. However, if only excess fat is found, the correction is considered purely aesthetic and must be paid for privately.
For mixed forms (95%), the removal of glandular breast tissue is covered by health insurance, while the removal of fat and any necessary breast lift is generally not included.
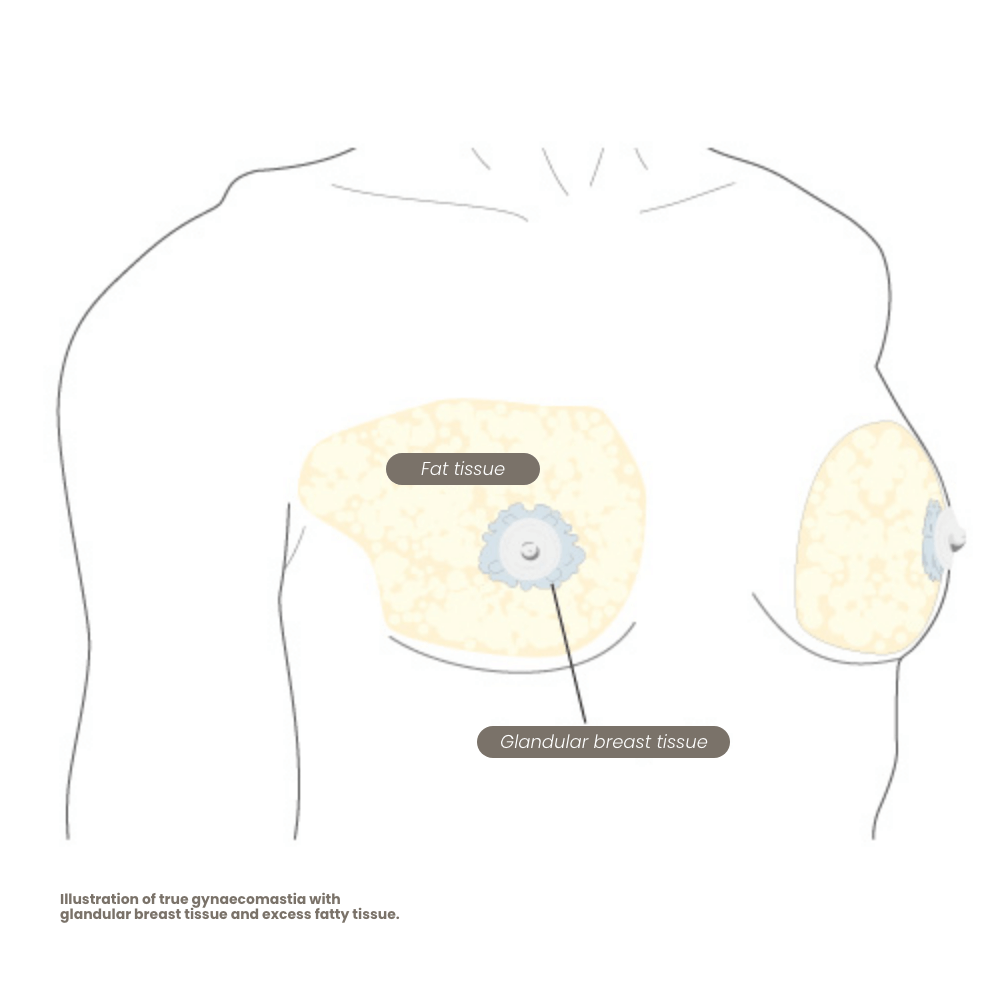
If the enlarged breast consists solely of excess fat (a condition known as lipomastia), it is almost always associated with being overweight. In such cases, weight loss and targeted physical activity can often improve the appearance. However, sometimes dieting and exercise are not enough, and the lipomastia persists even after reaching a normal weight. Those affected often feel unhappy, ashamed, and withdraw from social life because they do not feel masculine enough. In this case, the proven method of liposuction can provide a lasting improvement in body image and self-confidence by eliminating the stigma. If necessary, or if a large amount of fat has been removed, a (breast) lift may also be required.
If pathological causes for gynecomastia can be ruled out, there is generally nothing standing in the way of surgical correction.
A surgical correction of true gynecomastia includes the following steps:
- Removal of glandular breast tissue
- Removal of excess fat, if present
- Removal of excess skin
In cases of gynecomastia with significant fat and skin excess, the procedure can be combined with a breast lift. However, experience has shown that if a lift is necessary, it is better performed in a second operation — this is due to the risk of compromised blood circulation in the skin during simultaneous procedures. Regardless of this, in almost every correction of true gynecomastia (95%), liposuction is also required for aesthetic reasons. Only then can a smooth, harmonious transition to the surrounding tissue be achieved without any contour irregularities.
Nipple-Areola Complex
There are also cases of gynecomastia vera and lipomastia in which the diameter of the areola can or should be reduced if it is perceived as too large. For men, a diameter of 22–24 mm is considered ideal. However, this is not a general recommendation—every man should decide for himself whether the size of his areola is important to him and whether he wishes to have it reduced.
The degree of gynecomastia varies greatly from person to person, and in some cases, a simple liposuction combined with a breast lift may be appropriate—particularly when the male breast occurs only on one side.
Ultimately, every individual decides for himself to what extent the appearance bothers him and whether, and to what degree, he wishes to undergo breast correction.