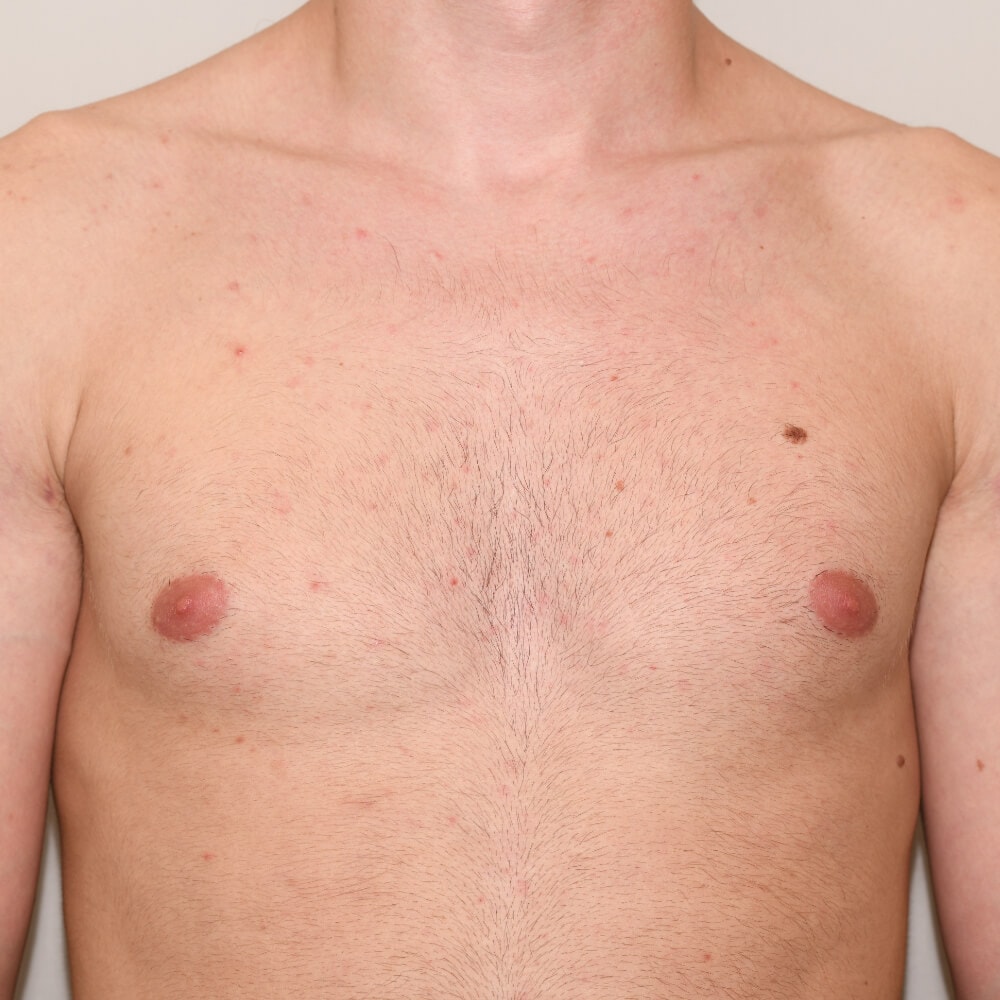
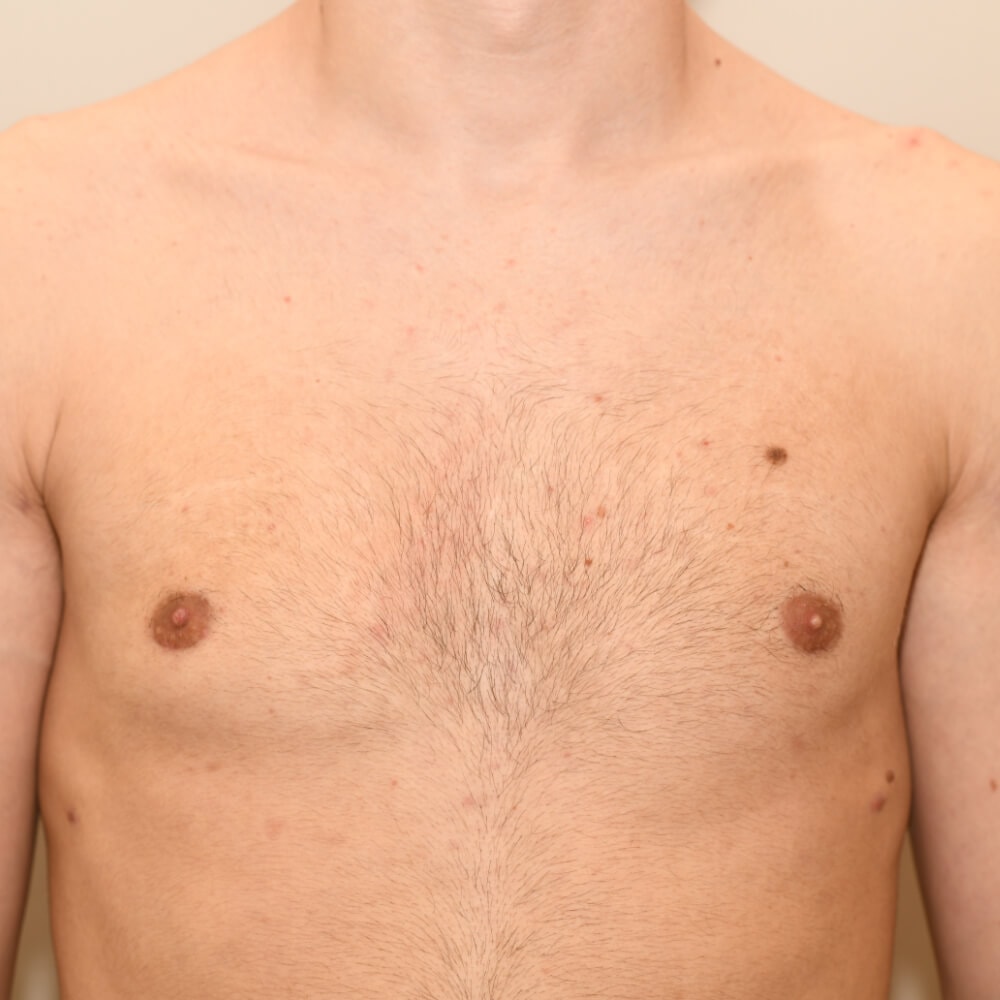
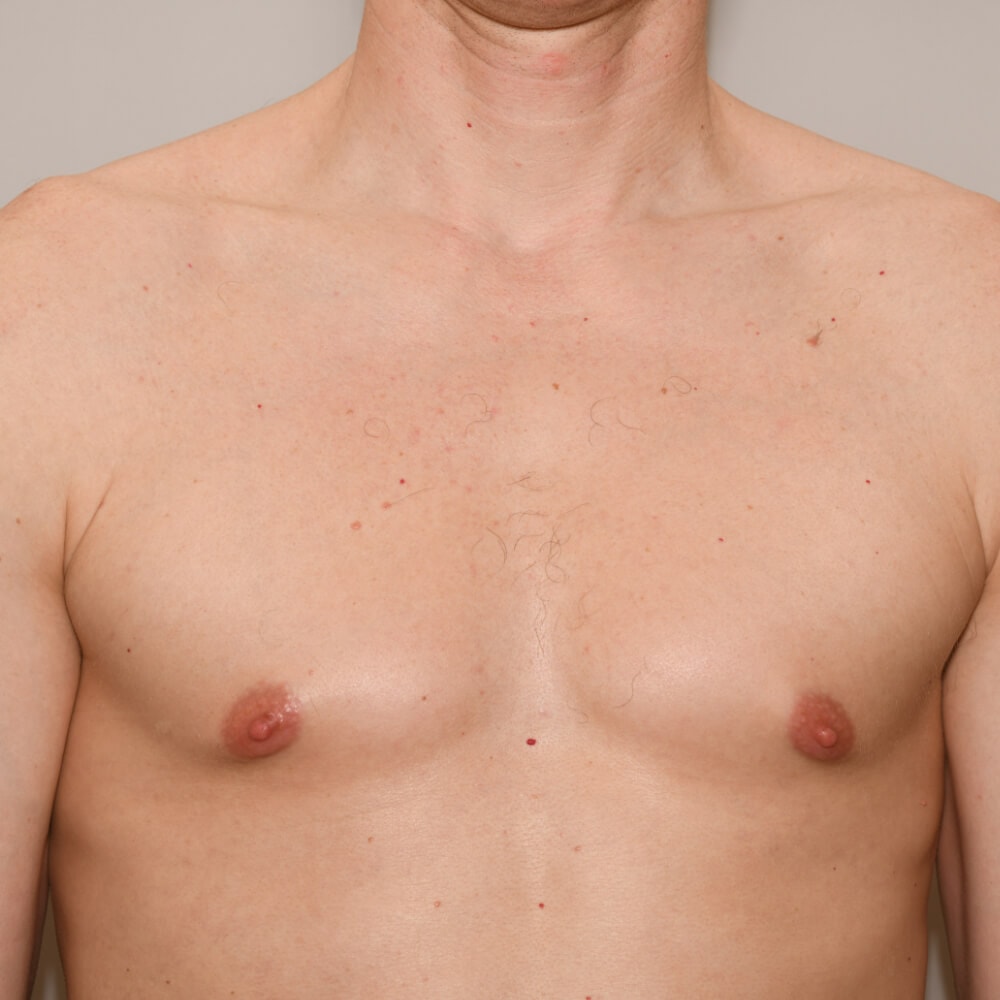
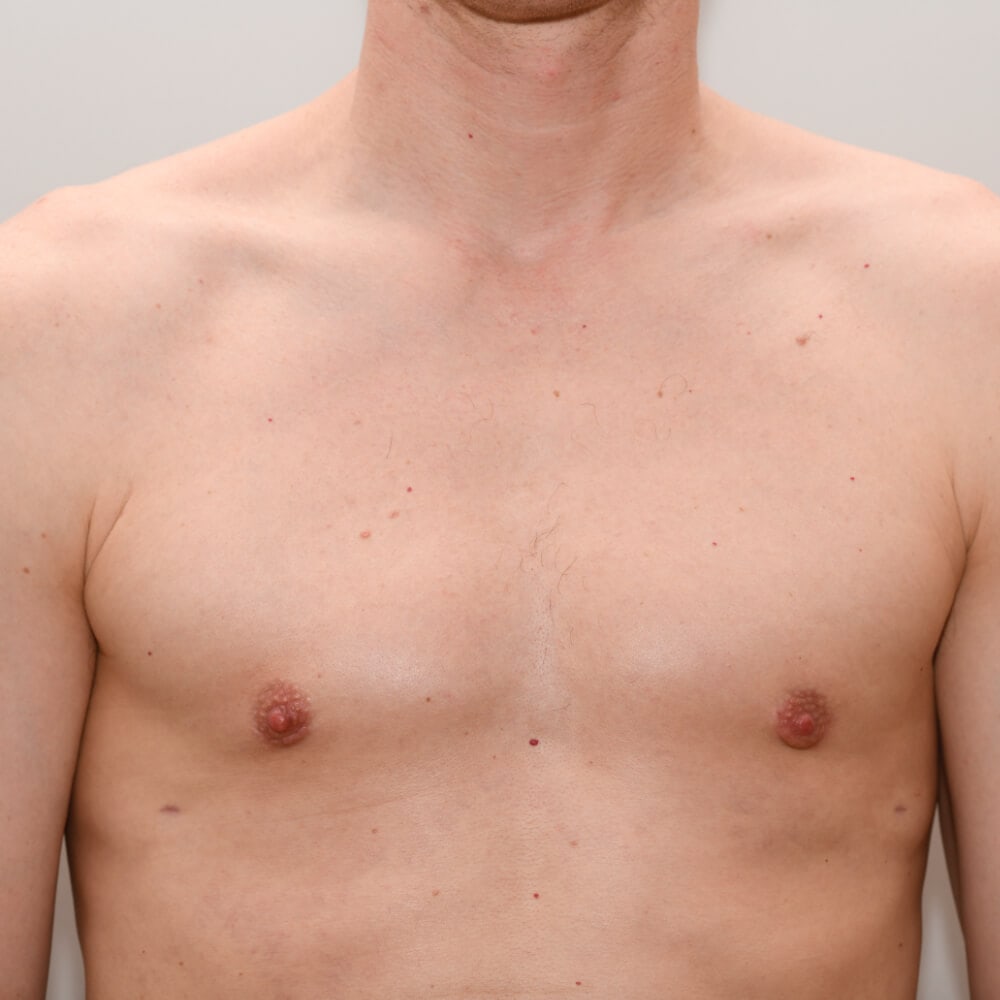
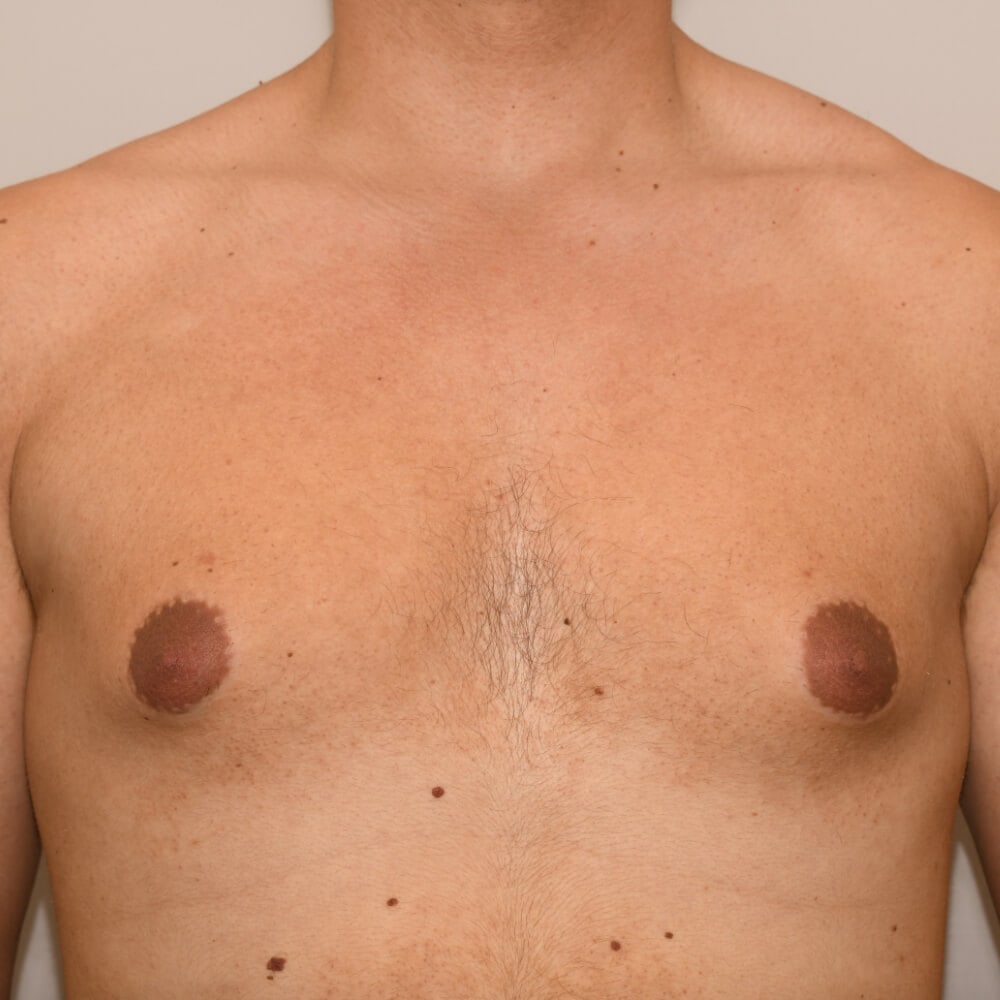
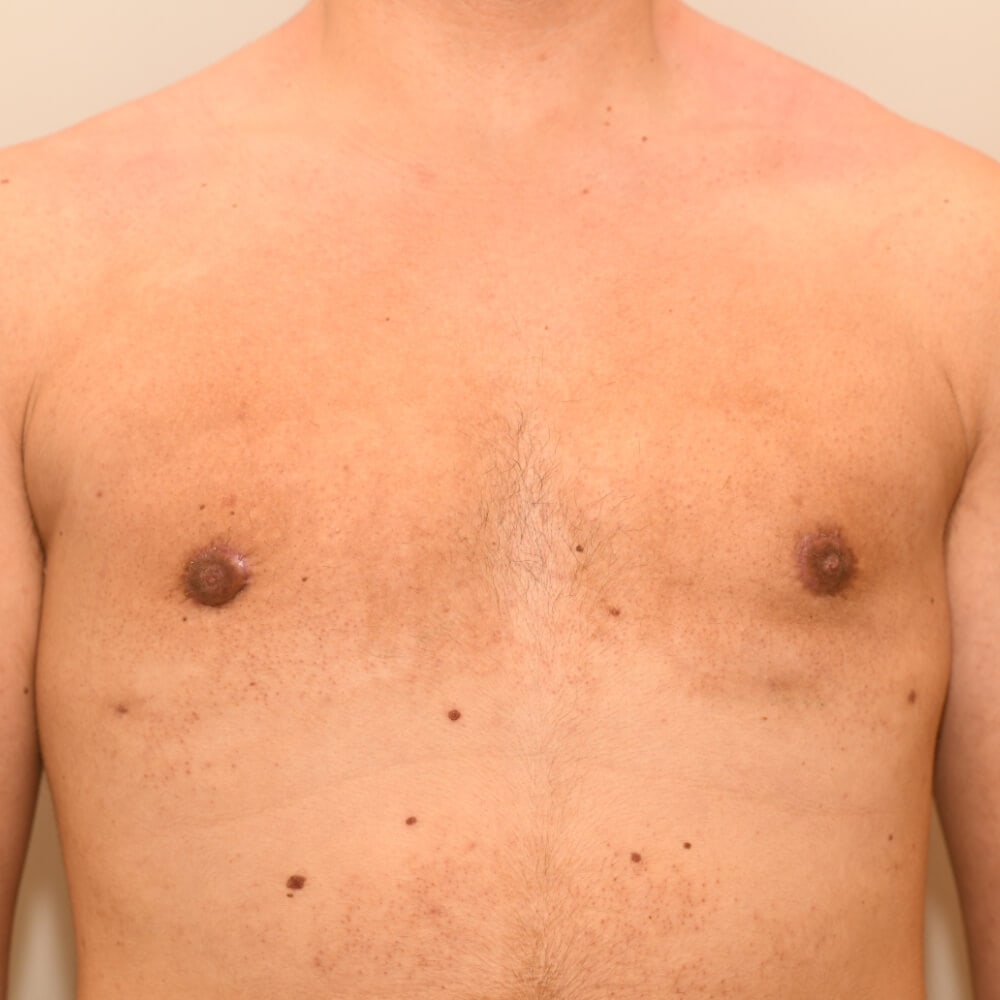
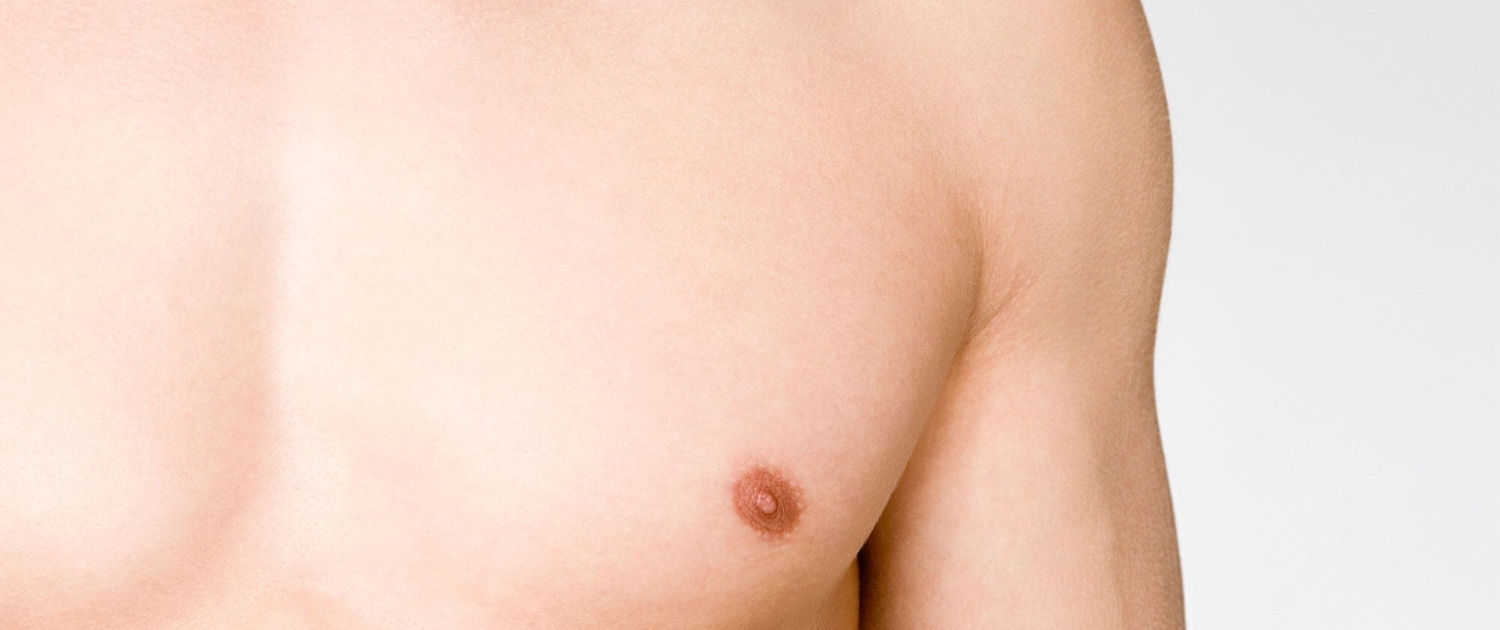
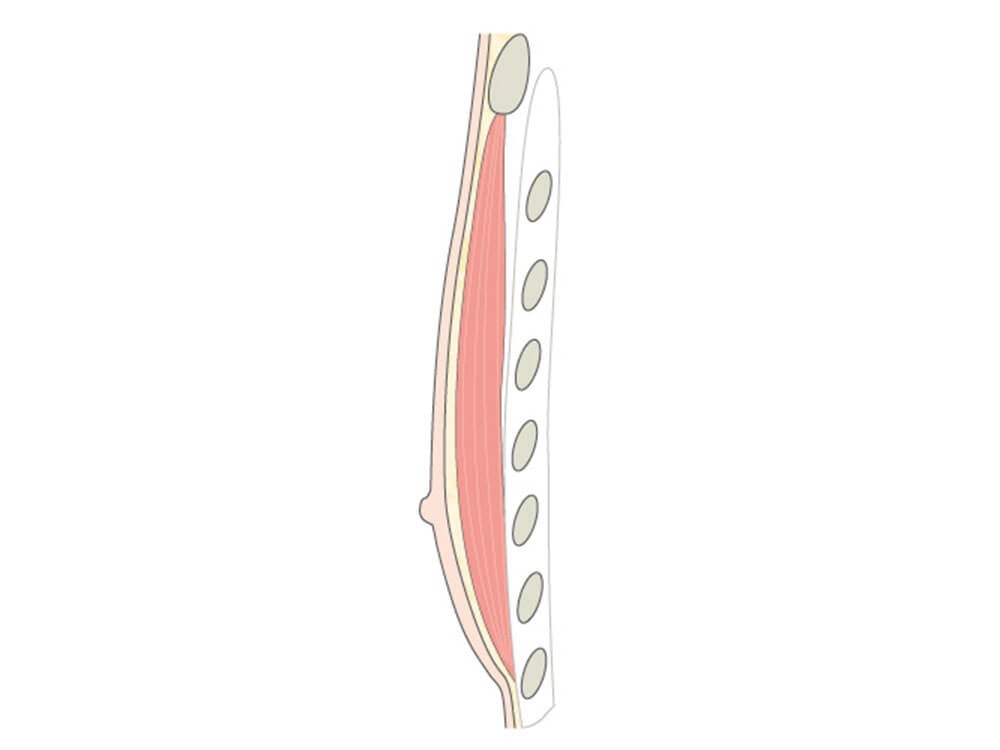
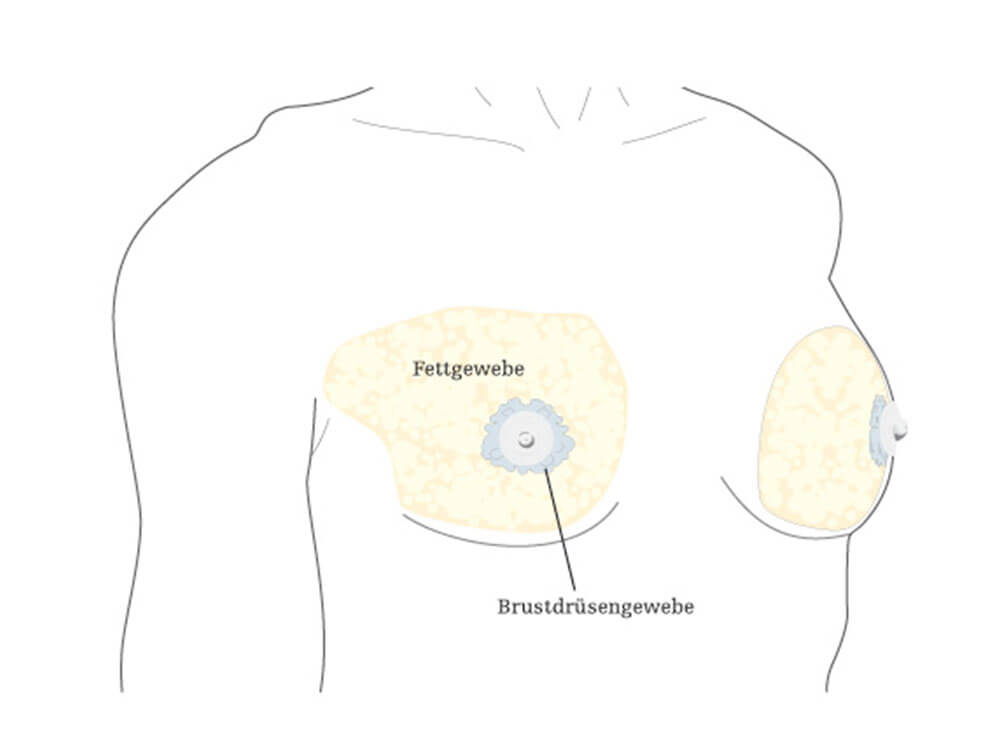
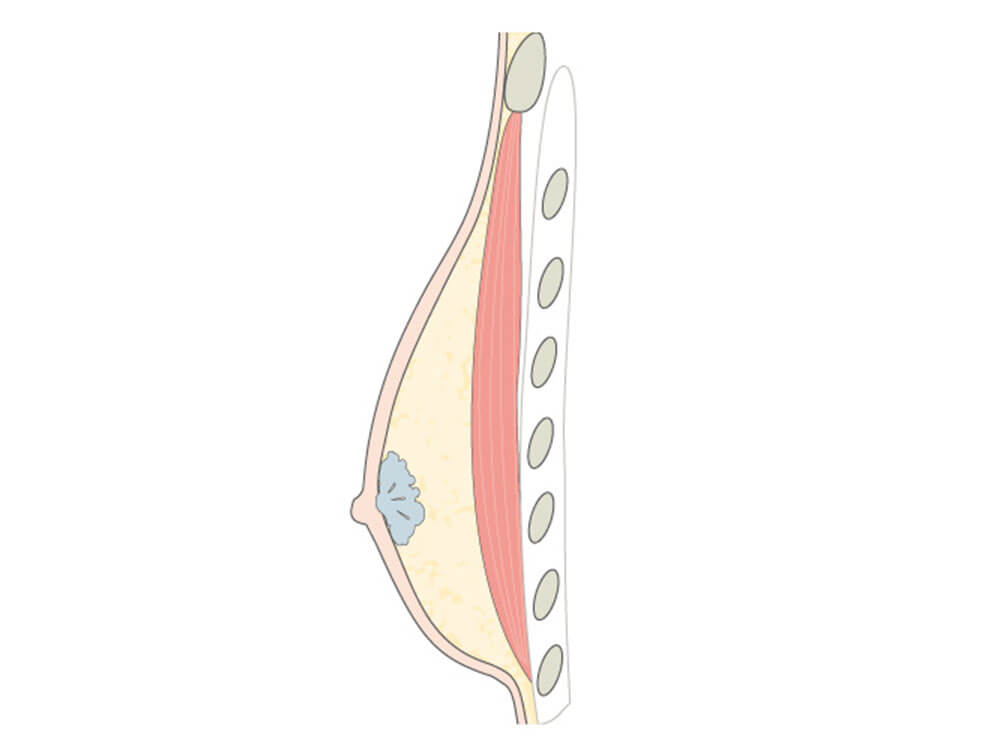
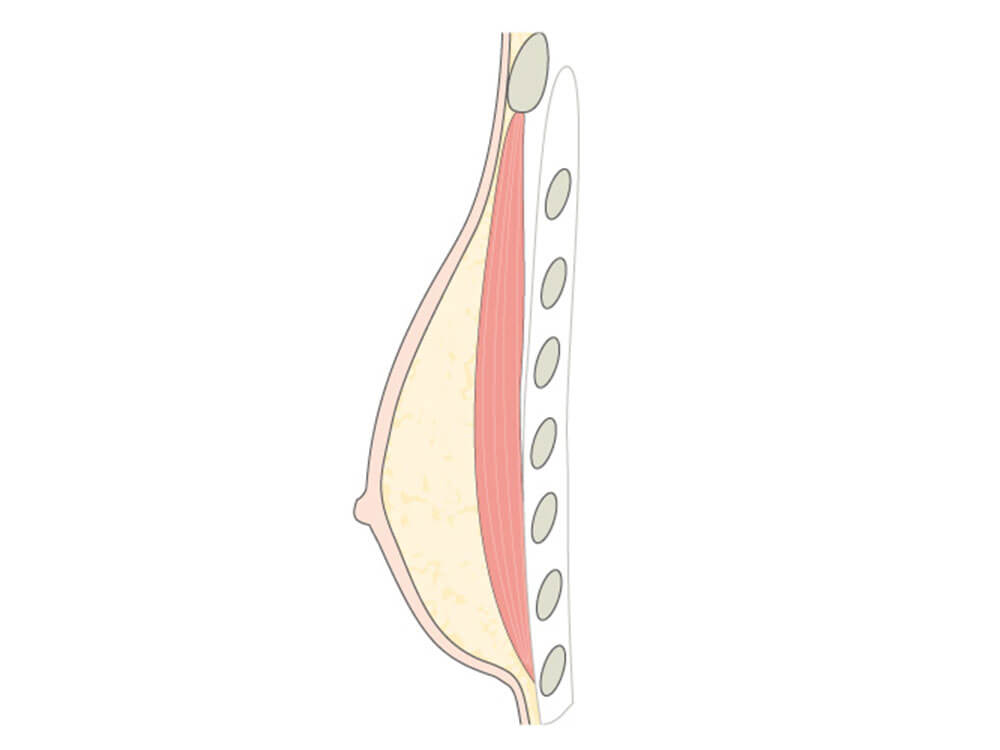
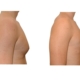
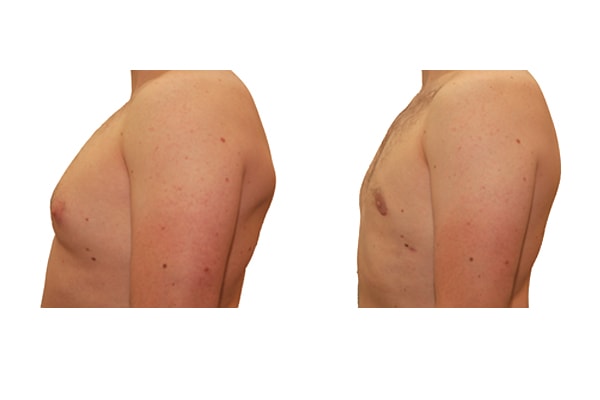
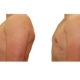
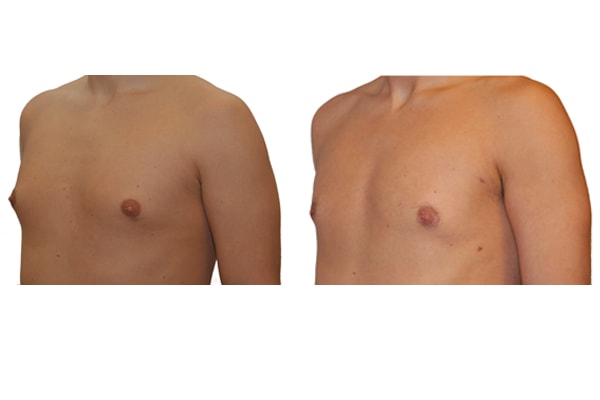
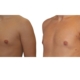
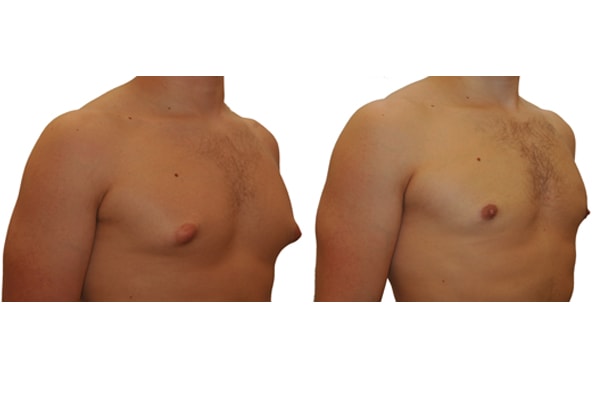
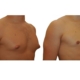
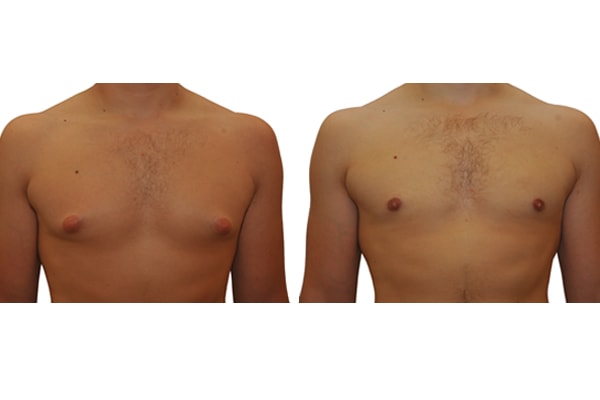
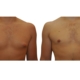
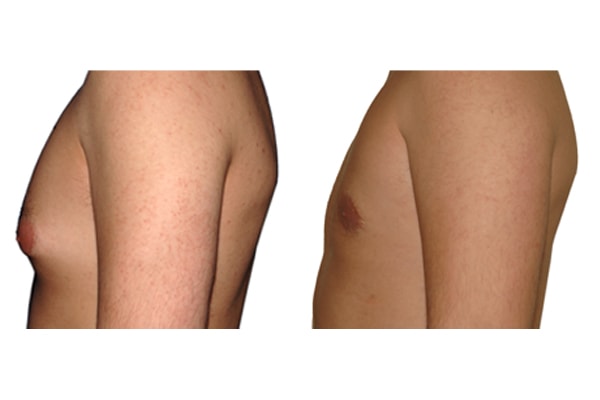
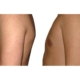
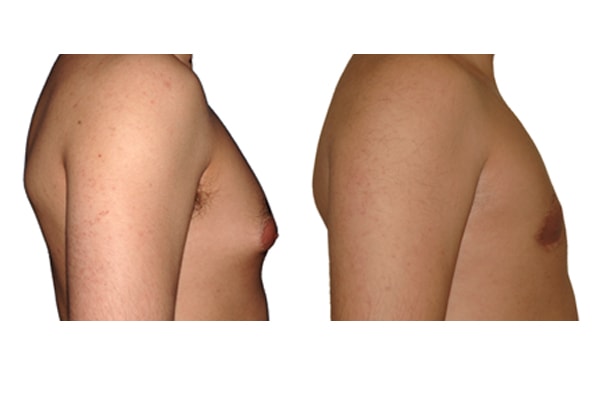
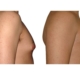
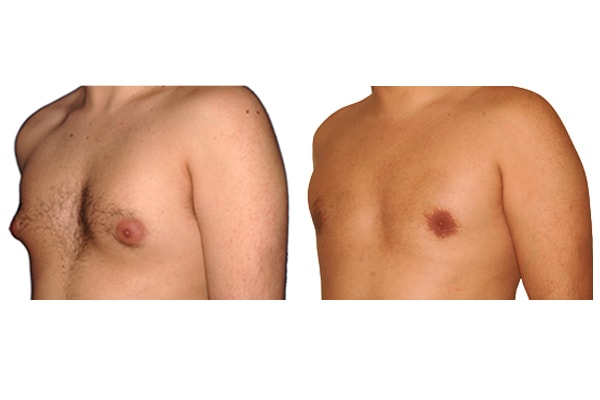
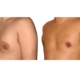
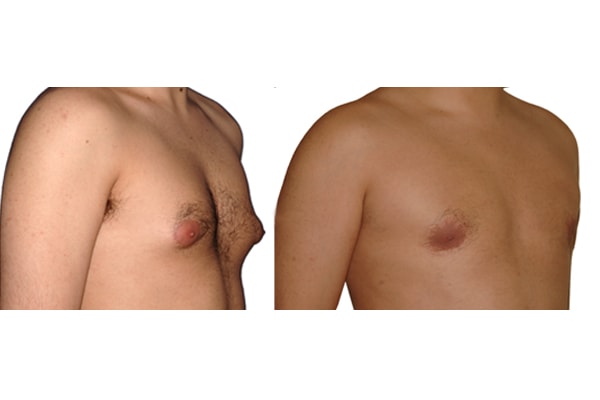
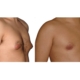
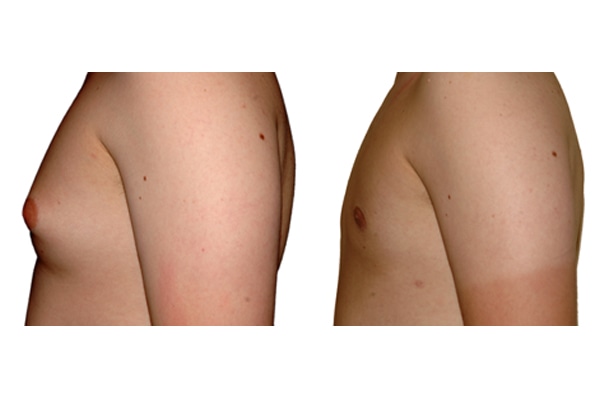
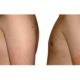
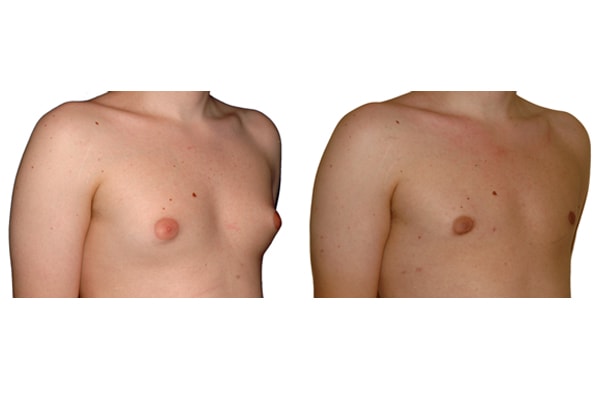
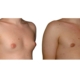
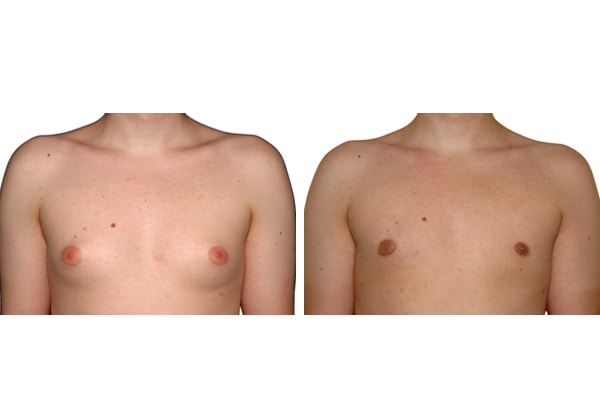
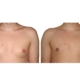
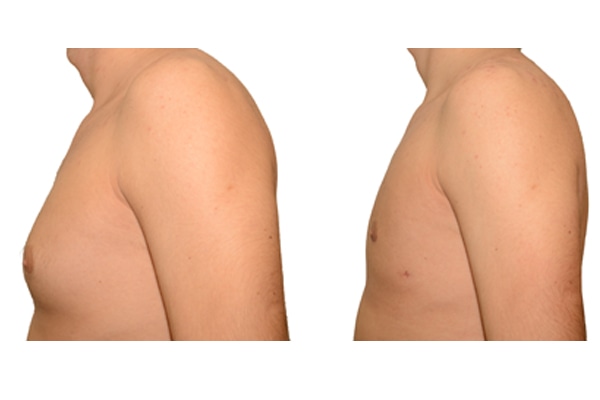
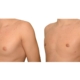
1. What is a gynecomastia?
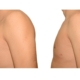
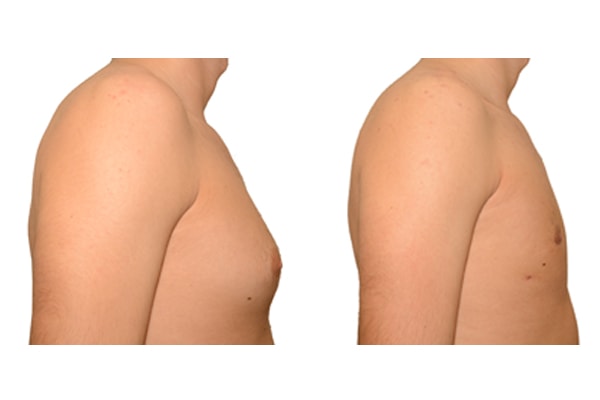
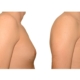
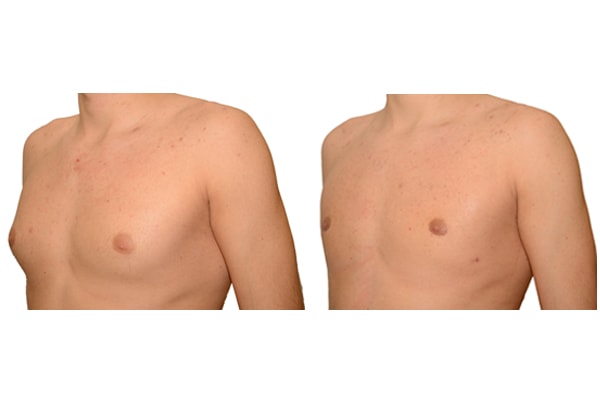
A true “gynecomastia” (gynaecomastia vera) refers to the presence of breast tissue in men. In addition, there may also only be increased fat present. If that is the case, this indicates a “false gynecomastia” (pseudogynecomastia, lipomastia). Most common, however, is a mixed form, where there is breast tissue and increased fat.
2. What causes the development of gynecomastia?
There are several causes that may lead to the development of gynecomastia: physiological causes, after massive weight loss and disease-related causes. Gynecomastia can also be caused by taking medication and drugs and other unknown causes. Unfortunately in 80% of the cases, both gynaecomastia and pseudo gynaecomastia, there are no medical explanations.
3. How many men are affected by gynecomastia?
In 50% of all men breast tissue can be found behind the areola. 1-2% of those affected have seen enlarged breasts.
4. Why do bodybuilders often suffer from a gynecomastia?
Bodybuilders often take anabolic steroids to support muscle increase . These are hormone-like substances that are similar to testosterone or its precursors. The way how gynecomastia develops in bodybuilders by anabolic steroids is relatively simple: the body tries to compensate for the increased testosterone levels and therefore increases the production of estrogen, which stimulates the growth of breast glandular tissue.
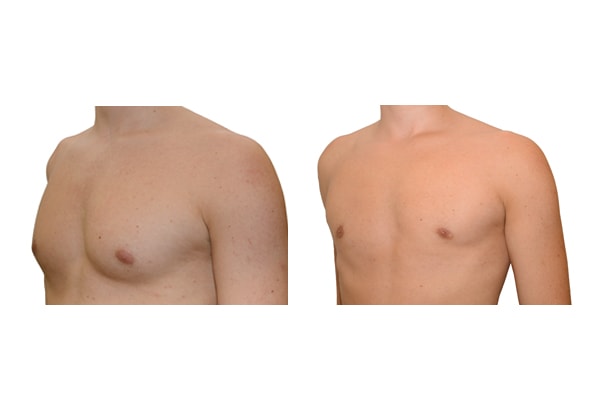
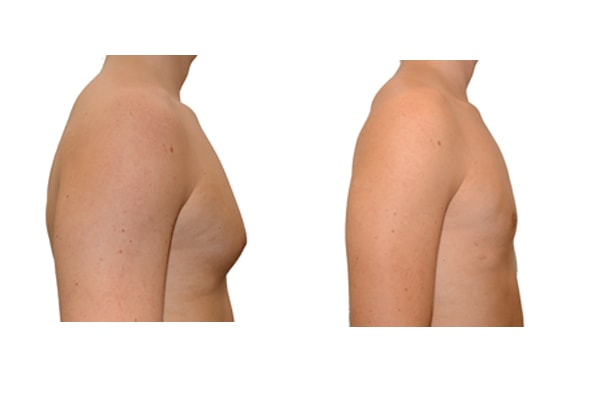
5. What surgical methods are there?
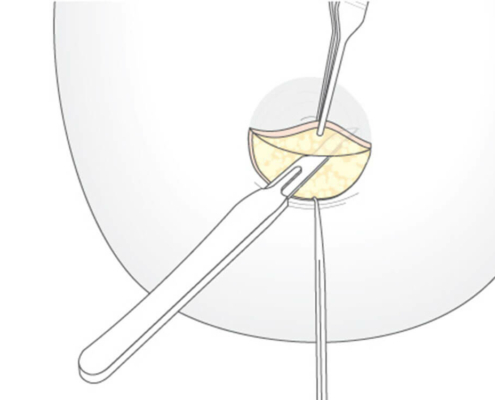
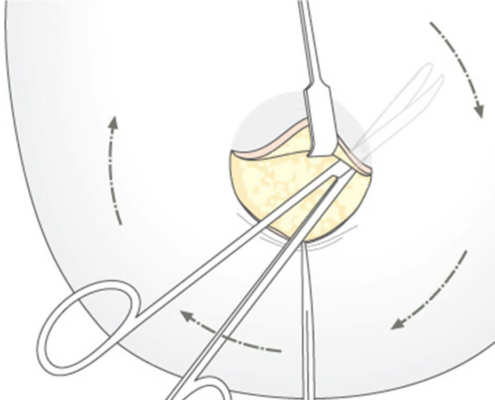
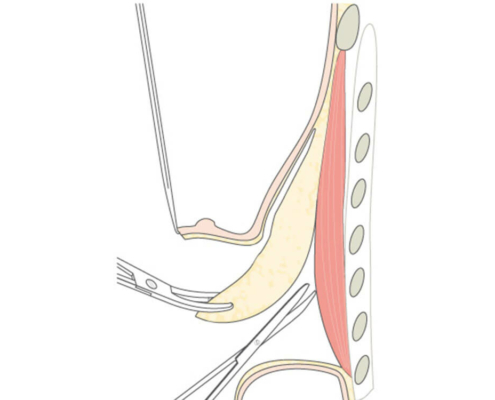
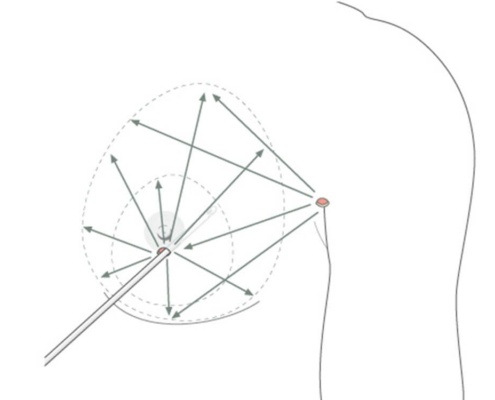
With small development and young age, the removal of the breast glandular tissue alone might often be enough. Additionally, if there is surplus of skin and more fat present, this must also be removed. Almost all patients require liposuction in the neighboring regions to improve contours and, in this sense, provide for an aesthetically pleasing result.
6. Can gynecomastia occur again after intervention?
If the complete removal of breast tissue can be achieved during surgery, a recurrent is ruled out. It is different with the fat: since not all fat cells can be removed, a new increase in breast size especially in case of weight gain of more than 5kg is unfortunately possible.
7. Does the health insurance cover the costs for the surgery?
The removal of the breast glandular tissue in true gynecomastia in Austria is paid for by the health insurance companies because men with breast glandular tissue, though much less than in women, can have breast cancer. Any necessary completing liposuction is unfortunately rarely covered.
8. What complications can occur?
Medical risks can include infection and bleeding, however; if surgery is properly performed, both are extremely rare. Aesthetic complications include asymmetry, steps and wrinkles and unsightly scars. Aesthetic complications can almost always be completely corrected.
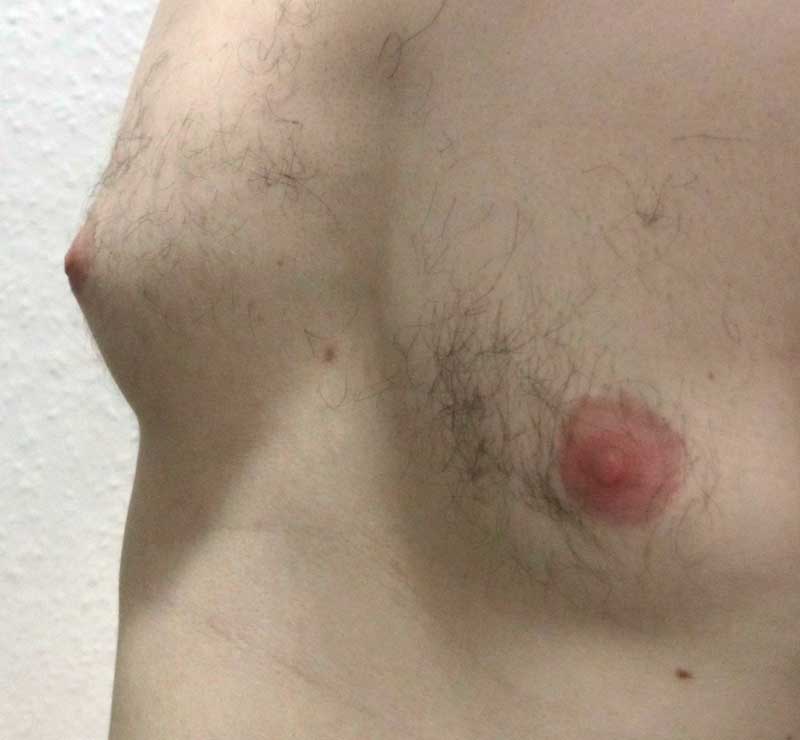
9. Where are the scars after gynecomastia-surgery?
In less severe cases, the scar is a small semicircle at the bottom of the areola to the border of the surrounding skin. In more severe cases, the scar runs around the areola. In severe cases the incision must be further extended laterally, the scar stretches out a few centimeters over the areola area.
10. When is one “operational” after gynecomastia surgery?
This depends largely on the extent of the operation (if tightening or a complementary liposuction is necessary). In general, it is back to normal after 7-10 recovery days.
11. Should I wear compression garment after the operation?
If concomitant liposuction was performed, the wearing of compression garment for the duration of 4-6 weeks is recommended. The compression underwear reduces bruising and supports the tissue to allow the skin to adjust to the new, reduced volume ratios better.
12. What are the long-term results after gynecomastia surgery?
Keep weight fluctuations less than 5 kg and long term results in general are excellent.